Safety In Acupuncture #3
Sample of Course Materials
Sample of course materials from section 1:
Pneumothorax
Do not needle deeply over the lungs. Puncturing of the lungs causes pneumothorax, a collapsed or partially collapsed lung wherein there is air or gas in the pleural space. Accidental needling through the lung is iatrogenic pneumothorax, caused by a medical examination or procedure. This may be due to a biopsy or improper acupuncture needling technique.
Onset of pneumothorax is marked by sudden sharp chest pain, shortness of breath and an unproductive cough. Low blood pressure accompanied by more severe symptoms may also occur such as upper back pain, exhaustion and the patient may turn blue due to low oxygen levels. Mild pneumothorax may resolve without medical intervention. However, the only correct protocol if there is a pneumothorax is to make sure that the patient is brought to an emergency medical facility immediately. Pneumothorax is a medical emergency. Severe cases may require surgery. Positive diagnosis is confirmed by X-Ray, CT scan or evaluation of arterial blood gases.
There are many points in common acupuncture practice that must be needled carefully to avoid pneumothorax. These points include the following:
• LU1, LU2
• ST11, ST13 ,ST14, ST15, ST16, ST17, ST18
• UB11, UB12, UB13, UB14, UB15, UB41, UB42, UB43, UB44, UB45
• KI23, KI24, KI25, KI26, KI27
• GB21
LU1, LU2
LU1 is located laterosuperior to the sternum at the lateral side of the 1st intercostal space, 6 cun lateral to the Conception Vessel. LU1 is 1 cun below LU2. LU1 is the front Mu pont of the Lung and is an intersection point of the Spleen channel. LU1 is indicated for the treatment of respiratory conditions including coughing and asthma. LU1 is needled 0.5 to 0.8 inches obliquely and laterally. Avoid the lungs by avoiding a medial or deep insertion.
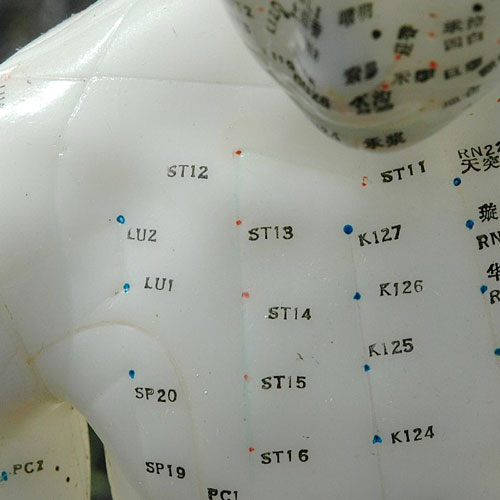
LU1, LU2, ST11-16, KI24-27 and other lung area points
LU2 is located in a depression below the acromial extremity of the clavicle, 6 cun lateral to the Ren Meridian. The point is located in the center of the depression formed by the deltopectoral triangle. LU2 benefits the lungs and is indicated for conditions including cough, asthma, chest pain and shoulder pain. This point is needled 0.5 to 0.8 inches laterally. Deep needling and medial needling is contraindicated and may cause...
More in course materials...
Sample from another section:
GB21
GB21 is located directly above the nipple midway between GV14 and the acromion at the highest point of the shoulder, at the crest of the trapezium muscle. GB21 is an intersection (meeting) point of the Triple Burner, Stomach and Yang Linking channels. GB21 is indicated for the treatment of apoplexy and hemiplegia due to stroke, mastitis, difficult labor, breast pain, scrofula, stiff neck and cervicalgia. This point is contraindicated for use during pregnancy.
Texts vary on needling depths and angles of insertion. The text Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion (Foreign Language Press, Beijing) notes that this point is needled perpendicularly 0.3 to 0.5 inches. Note the shallow insertion recommendation. The text does not mention the pinching-grabbing needle technique to the skin and muscle often taught in acupuncture schools as a precautionary measure. Needling techniques are beyond the scope of this course and are generally taught in live seminars or interactive environments. However, a discussion of needling methods from an academic perspective is important given that there is a high risk of pneumothorax if this acupuncture point is needled perpendicularly or deeply.
The text Acupuncture, A Comprehensive Text (Eastland Press) notes that the needling method for GB21 is “Straight insertion, 0.5-1 unit. Sensation: dissension and soreness extending to shoulder region. CAUTION: Care should be taken not to insert needle too deeply, to avoid puncturing the lung.” GB21 is at the apex of the lungs. In some individuals, the apex is less than 1 cun under GB21 and a perpendicular insertion of 1 inch, cun or unit would cause pneumothorax. Therefore, the needle depth limit set in…
More in Course Materials...
Sample from another section:
General Needle Safety
A needle is consider “stuck” when the practitioner cannot rotate, lift or thrust it. This may be due to a local muscles spasm, nervous tension, excessive twirling of a needle in one direction or if the patient has changed position. One method is to wait for the area to relax and then remove the needle. Another method is have the patient resume the…
More in course materials...
Sample from another section:
Cell Phones and Distractions
Patients changing posture becomes challenging in the modern environment filled with distractions such as cell phones. Patients often reach for the cell phone to answer a call or use the device in some other fashion during the acupuncture treatment. Listening to a call is problematic in several ways that affect safety.
Patients may place the phone beside the ear thereby shifting points on the hands, arms and ears. At the Healthcare Medicine Institute (HealthCMi), we have received reports from acupuncturists of...
More in course materials...
Sample from another section:
Avoiding Syncope & Adverse Reactions
Lighter treatments using fewer needles are indicated for patients who have not eaten prior to treatment, have overeaten, are intoxicated or exhausted or are very weak. Patients who are hungry during an acupuncture treatment are more likely to experience adverse effects. In all of these cases, it may be indicated to reschedule the acupuncture appointment.
Fainting may occur if the patient’s qi is weak or if the patient is stressed or hungry. Strong manipulation of the needles that exceeds the patient’s constitutional ability to handle the stimulation may cause fainting. Common scenarios are the use of many needles, strong needle stimulation or the use of strong needle techniques when the patient is seated. Fainting is more likely in the seated position than...
More in course materials...
Sample from another section:
Cleansing the Area
According to many clean field guidelines, 70% ethyl or isopropyl alcohol is the correct agent to be used to cleanse the skin with a cotton ball prior to acupuncture needling. The CCAOM (Council of Colleges of Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine) advises…..
More in course materials...
Sample from another section:
Medical Records
Acupuncturists are required by law to maintain medical records for several years in most states and countries. Additional requirements for medical record retention may be made by malpractice insurance carriers. Health insurance companies may also require…
More in course materials...
Sample from another section:
Biomedical Waste
Many of the legal parameters discussed in this course differentiate rules and regulation between countries and states. Biomedical sharps waste, however, is often regulated by additional county rules.
In California, the following rule applies for small quantity generators of medical waste:
For the two types of medical waste, biohazardous and sharps waste, the storage times do differ. A facility that generates less than 20 pounds of biohazardous waste per month may…
More in course materials…