Acupuncture reduces anxiety levels. Researchers from Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine investigated the efficacy of electroacupuncture at Huatuojiaji acupoints combined with scalp acupoints for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). 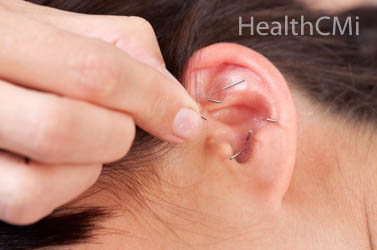 The results were compared with a traditional acupuncture group and a drug therapy group. The electroacupuncture group had a total effective rate of 96.7% and the traditional acupuncture group achieved an 83.3% total effective rate. The drug therapy group, receiving paroxetine, achieved a 73.3% total effective rate. Based on the findings, the researchers conclude that electroacupuncture at Huatuojiaji and scalp acupuncture points is effective for the treatment of GAD.
The results were compared with a traditional acupuncture group and a drug therapy group. The electroacupuncture group had a total effective rate of 96.7% and the traditional acupuncture group achieved an 83.3% total effective rate. The drug therapy group, receiving paroxetine, achieved a 73.3% total effective rate. Based on the findings, the researchers conclude that electroacupuncture at Huatuojiaji and scalp acupuncture points is effective for the treatment of GAD.
GAD is characterized by excessive worry and a feeling of anxiousness. Symptoms include the inability to relax, difficulty concentrating, startling easily, insomnia, headaches, exhaustion, muscle tension, nausea, and irritability. There may be concomitant excessive sweating, difficulty swallowing, twitching, frequent urination, palpitations, and lightheadedness.
All three approaches investigated delivered significant positive patient outcomes. Interestingly, both forms of acupuncture that were studied outperformed the drug therapy. The medication used was paroxetine hydrochloride tablets, 20 mg, taken twice per day. Brand names for paroxetine hydrochloride include Paxil, Brisdelle, and Pexeva. Paroxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) often prescribed for depression, anxiety, and PTSD. For the electroacupuncture group, 1.5” filiform needles of gauge 30 were applied to Huatuojiaji points slanted medially to a 0.5” to 1” depth. For scalp acupuncture, needles were applied to the emotional area as described by Wang et al.
Results were based on the Hamilton Anxiety Scale. Symptoms evaluated included those related to the muscular, nervous, cardiovascular, respiratory, alimentary tract, urinary, reproductive, and autonomic nervous systems. Evaluations included changes in anxiety, nervousness, fear, insomnia, cognitive function, depression, and conversational behavior. The results indicate that electroacupuncture is effective in the reduction of anxiety.

In a related study, researchers from Hebei United University conclude that acupuncture relieves test anxiety. This is a type of performance anxiety related to taking exams. It involves several components including fear of failure and a feeling of unpreparedness. Two types of acupuncture were found effective in relieving test anxiety, wrist-ankle acupuncture and auricular acupuncture. The wrist-ankle acupuncture achieved an 84.2% total effective rate and the auricular acupuncture achieved an 82.8% total effective rate.
The wrist-ankle acupuncture group received needling at acupoints in the upper 1 zones. The auricular acupuncture was applied to heart, shenmen, endocrine, adrenal gland, and subcortex acupoints. The Sarason Test Anxiety Scale (TAS) and an autonomic function test were used to assess the anxiety severity before and after treatment. Based on the data, both types of acupuncture were determined safe and effective for the treatment of test anxiety.
References:
Sheng, G. B., Li, H. & Tang, Y. (2015). Clinical Observation on the Treatment of Electroacupuncture JiaJi Acupoint Therapy Combined with Scalp Acupuncture for Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion. 31 (5).
Wang, W., Zhou, G. B. & Yu, Z. S. (2003). Dr. Yu Zhi Shun scalp acupuncture treatment clinical experiences. China TCM Modern Remote Education. (6): 28-31.
Tian, W., Yang, N., He, Q. R., Yang, T., Cui, J. M. & Wang, H. B. (2015). Efficacy of Wrist-ankle Acupuncture plus Auricular Point Sticking for Pre-exam Anxiety Syndrome.
Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion. 34 (4).
Bo, Y. & Chen, X. W. (2004). Effectiveness of Auricular Seed-pressing Therapy in Treating Secondary Pupils Pre-exam Anxiety Syndrome. Chinese Doctors. 18 (6): 541.
Tian, W., Yang, N., He, Q. R., Yang, T., Cui, J. M. & Wang, H. B. (2015). Efficacy of Wrist-ankle Acupuncture plus Auricular Point Sticking for Pre-exam Anxiety Syndrome.
Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion. 34 (4).
Bo, Y. & Chen, X. W. (2004). Effectiveness of Auricular Seed-pressing Therapy in Treating Secondary Pupils Pre-exam Anxiety Syndrome. Chinese Doctors. 18 (6): 541.


