New research shows that acupuncture has an antioxidant effect in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Mounting evidence shows that oxidative stress contributes to the progression of Parkinson’s disease. The new research shows that 100 Hz electroacupuncture applied to acupuncture points St36 (ZuSanLi) and Sp6 (SanYinJiao) has a neuroprotective effect on the brain because electroacupuncture is antioxidant. This study includes contributions from Xibin Liang, a researcher from the Department of Neurology and Neurological Sciences at Stanford University located in Palo Alto, California.
Researches determined that stimulation of St36 and Sp6 with electroacupuncture protects the brain by creating antioxidative and antiapoptosis effects. The electroacupuncture protected a part of the mid-brain called the substantia nigra. The substantia nigra is an important part of the brain in controlling movement. Parkinson’s disease is caused by the deterioration of dopaminergic neurons in a part of the mid-brain called the substantia nigra pars compacta. The substantia nigra pars compacta supplies the basal ganglia (an area of the brain involved with motor action) with dopamine. Dopamine is an essential nutrient for the brain and has neurotransmitter functions. Dopamine is also a precursor for norepinephrine and epinephrine.
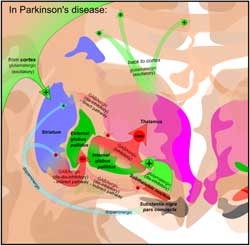
To view a larger image click the following: Acupuncture CEU Image
Reference:
1. Wang H, Pan Y, Xue B, Wang X, Zhao F, et al. (2011) The Antioxidative Effect of Electro-Acupuncture in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease.
2. Photo: Mikael Häggström, based on images by Andrew Gillies/User:Anaru and Patrick J. Lynch.

