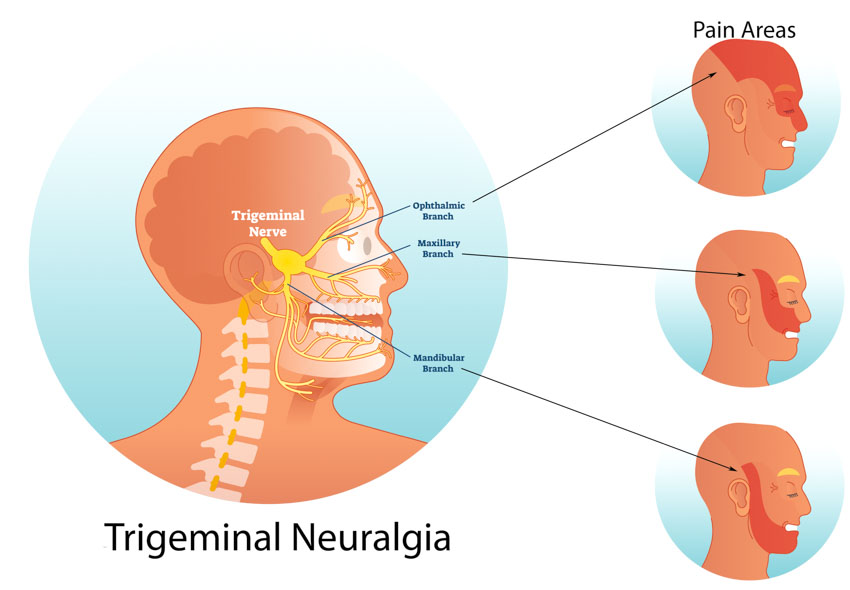
Acupuncture increases the efficacy of drug therapy for the relief of trigeminal neuralgia by 20%. Researchers from the Affiliated Huzhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of the Zhejiang Chinese Medical University conclude that acupuncture combined with carbamazepine delivers consistent positive clinical outcomes for patients with trigeminal neuralgia, a pain disorder of the face involving the 5th cranial nerve.
Carbamazepine monotherapy produced a 70.0% total effective rate. Adding acupuncture to the treatment protocol increased the total effective rate to 90.3%. [1] Carbamazepine is an anticonvulsant and analgesic benzodiazepine drug used for the treatment of seizures and nerve pain. In addition, 6-month follow-up examinations confirm that acupuncture produces lasting and significant clinical results.
The results were measured with VAS scoring, pain frequency, and the MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36) scoring at the completion of all medical treatments. SF-36 is constructed to assess the following eight parameters: physical activities, social activities, physical role activities, bodily pain, mental health, emotional role activities, vitality, and general health perceptions. Lower scores in SF-36 assessments denote a lower quality of life.
Both groups (i.e., drug monotherapy, acupuncture plus drugs) showed significant improvements across all testing measures after completion of treatments. However, the acupuncture plus drugs group produced superior patient outcomes. The VAS score was 5.07 ±0.83 in the acupuncture plus drugs group, and 5.13 ±0.88 in the drugs only group. The pain frequency was 8.21 ±1.89 times per week in the acupuncture plus drugs group, and 10.14 ±2.13 times per week in the drugs only group. The SF-36 score was 140.26 ±13.58 in the acupuncture plus drugs group, and 121.21 ±15.16 in the drugs only group.
Another set of measurements were made in a 6-month follow-up for all patients in the study. The results indicate that acupuncture plus drugs produces lower VAS scores and symptom frequency and higher SF-36 scores compared with the drugs only group. The VAS score was 2.37 ±0.72 in the acupuncture plus drugs group, and 4.26 ±1.03 in the drugs only group. The pain frequency was 3.00 ±2.74 times per week in the acupuncture plus drugs group, and 4.26 ±1.03 times per week in the drugs only group. The SF-36 score was 180.51 ±15.25 in the acupuncture plus drugs group, and 150.59 ±12.38 in the drugs only group. There was a significant difference between the two groups for all parameters, indicating that acupuncture increases clinical efficacy in the long-term.
Design
A total of 61 patients were treated and evaluated in the study. All patients were diagnosed with trigeminal neuralgia. They were randomly divided into an acupuncture plus drugs group and a drugs only group, with 31 and 30 patients in each group respectively. Inclusion criteria were as follows. All participants were diagnosed with trigeminal neuralgia according to the third edition of the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3). In addition, patients participating in the study met the following inclusion criteria:
- Frequent attacks of pain
- 18–80 years of age
Exclusion criteria were applied. Patients having the following conditions did not participate in the study:
- Severe primary and comorbid heart, liver, kidney diseases that affect drug metabolism
- Infection, ulcers, scars and other abnormalities of acupuncture sites
- Malignant tumors, blood system diseases, cerebrovascular disorders, and other serious life-threatening conditions
- Pregnant or lactating
- Conditions that affect observation or laboratory indicators
The statistical breakdown for each randomized group was as follows. The acupuncture plus drugs group was comprised of 13 males and 18 females. The average age in the acupuncture plus drugs group was 54 years. The average course of disease in the acupuncture plus drugs group was 4.74 years. The drugs only group was comprised of 12 males and 18 females. The average age in the drugs only group was 59 years. The average course of disease in the drugs only group was 6.62 years. There were no significant statistical differences in terms of gender, age, and course of disease relevant to patient outcome measures.
Treatment
Both groups received identical drug therapy. The dose of carbamazepine started at 100 mg and increased by 100 mg every day until pain control was achieved. The average dose was 400–800mg per day. The maximum dose was 1200 mg. After reaching the maximum, the dose was gradually decreased until the minimum effective dose was obtained. The drug was taken twice per day. Each treatment course consisted of 7 days of drug treatment. All patients received 4 treatment courses in total. The primary acupoints selected for acupuncture treatment were the following:
- Heart (auricular acupuncture)
- Lung (auricular acupuncture)
- Shenmen (auricular acupuncture)
- LI20 (Yingxiang)
- EX-HN-22 (Anmian)
- ST36 (Zusanli)
- ST2 (Sibai)
- ST4 (Dicang)
- ST7 (Xiaguan)
- ST44 (Neiting)
- LV3 (Taichong)
- Ashi points
Additional acupoints were selected on an individual symptomatic basis. For ophthalmic pain, the following acupoints were added:
- BL2 (Cuanzhu)
- GB14 (Yangbai)
For maxillary pain, the following acupoints were added:
- ST3 (Juliao)
- SI18 (Quanliao)
For mandibular pain, the following acupoints were added:
- CV24 (Chengjiang)
- ST6 (Jiache)
After disinfection of the acupoint sites, a 0.25 × 40mm disposable filiform needle was inserted perpendicularly into each acupoint with a high needle entry speed. The attenuating (xie) technique was applied. Once a deqi sensation was obtained, the needles were retained for 30 minutes. The treatment was conducted once per day, 6 times per week. Each treatment course consisted of 6 days of acupuncture treatments, followed by a 1-day break. All patients received 4 treatment courses in total.
Evaluation
Patients were evaluated before and after the full treatment course. First, all patients underwent Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) assessments before and after their treatments. VAS is a measurement instrument used to measure pain intensity. Second, pain frequency was documented. Third, quality of life was measured according to the MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). After completion of treatment, the efficacy rates for each patient were categorized into 1 of 4 tiers:
- Recovery: pain stopped and did not recur during the 6 months of follow-up
- Significantly effective: pain was significantly relieved and pain frequency was reduced by 75%
- Effective: pain was relieved and pain frequency was reduced by 50%.
- Ineffective: no change in pain and pain frequency was reduced by less than 25%
Summary
The results indicate that acupuncture plus drug therapy is more effective than drug monotherapy. Carbamazepine monotherapy produced a 70.0% total effective rate and acupuncture plus carbamaepine produced a total effective rate of 90.3%. The study mentioned in this report demonstrates that acupuncture is safe and effective for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Important features of TCM (Traditional Chinese Medicine) protocols is that they produce both short-term and long-term patient outcomes without causing significant adverse effects.
Reference
[1] Pan ZQ, Fu RY, Lin XM. Clinical Study on Mind-regulating Acupuncture in Treating Primary Trigeminal Neuralgia [J]. Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, 2017, 36(9):1069-1073.


